Dental implants have revolutionized modern dentistry, offering a reliable and long-term solution for missing teeth. When a tooth is lost due to decay, gum disease, or injury, it affects more than just the appearance of your smile.
Missing teeth can lead to difficulties in chewing, speech problems, and even the gradual shifting of surrounding teeth.
Over time, this can cause jawbone deterioration, facial sagging, and other oral health complications.
Traditionally, dental bridges were the most common treatment for replacing missing teeth. Bridges remain a popular option today because they are cost-effective and quicker to place.
However, dental implants have gained increasing popularity due to their durability, natural appearance, and ability to preserve jawbone health.
Choosing between a dental implant and a bridge can be challenging since both options have unique advantages and limitations.
Your decision should depend on factors like oral health, budget, and long-term goals.
Dental Implants vs Bridges Which Is the Better Option
In this guide, we will explain everything you need to know about dental implants and bridges, including their differences, costs, benefits, and which option may be best for your specific needs.
Why Tooth Replacement Matters
Tooth loss is a common issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It can occur due to several reasons, such as gum disease, tooth decay, injury, or aging.
When a tooth is lost, the gap it leaves behind does more than just affect the appearance of a person’s smile. It can have a serious impact on overall oral health.
The surrounding teeth may begin to shift toward the empty space, which causes misalignment and bite problems.
Over time, this can lead to uneven wear, jaw discomfort, and an increased risk of gum disease.
Chewing and speaking can also become difficult when teeth are missing.
In addition to these problems, the jawbone in the area of the missing tooth begins to deteriorate because it no longer receives the stimulation it once did during chewing.
Studies have shown that jawbone density can decrease by as much as twenty-five percent within the first year after a tooth has been removed.
This loss of bone can change the shape of the face, leading to a sunken appearance and more complex dental issues in the future.
Replacing missing teeth as soon as possible is essential not only to restore the look of your smile but also to maintain proper oral function and prevent further problems.
Dental implants and dental bridges are the two most common solutions for replacing missing teeth, and each has its unique benefits and challenges.
What Are Dental Implants?
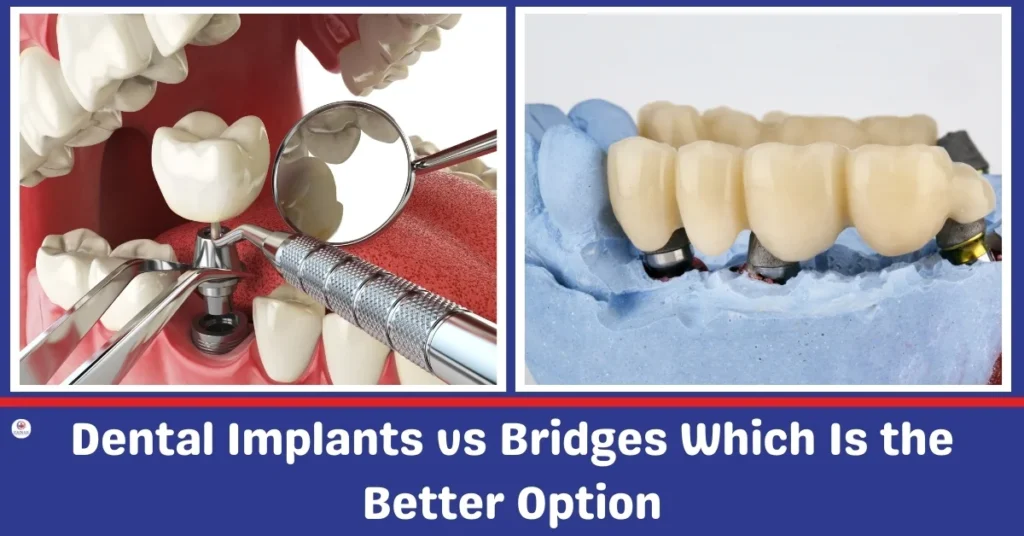
Dental implants are one of the most advanced solutions available for replacing missing teeth. They are designed to act as artificial tooth roots and are usually made from titanium or zirconia.
These materials are highly biocompatible, which means they can fuse naturally with the jawbone through a process called osseointegration.
Once this fusion is complete, the implant becomes a stable and secure foundation for a replacement tooth, known as a crown.
The implant system is typically made up of three parts. The implant post is surgically placed into the jawbone and serves as the root of the new tooth.
An abutment, which is a small connector, is then attached to the top of the implant post.
Finally, a custom-made crown is fitted onto the abutment, creating a natural-looking and functional replacement for the missing tooth.
The process begins with a detailed consultation and imaging, such as X-rays or 3D scans, to determine the patient’s bone health. If there is enough bone density, the implant is placed during a minor surgical procedure.
Healing usually takes three to six months as the bone integrates with the implant. Once the area has healed fully, the permanent crown is placed.
Dental implants are considered a long-term or even permanent solution, and with proper care, they can last for decades.
What Are Dental Bridges?
Dental bridges are a traditional method for replacing missing teeth. A bridge is a fixed restoration that consists of a false tooth, called a pontic, held in place by crowns on the teeth adjacent to the gap.
These neighboring teeth serve as anchors to support the bridge.
The process of getting a dental bridge begins with preparing the surrounding teeth. This preparation involves reshaping them by removing some of their enamel so the crowns can fit securely.
Once the teeth are ready, impressions are taken and sent to a dental lab, where the custom bridge is created.
During a follow-up visit, the bridge is fitted and cemented in place.
Dental bridges do not require surgery and can usually be completed in two to four weeks. They restore the appearance of a smile and improve function quickly.
However, bridges do not replace the tooth root or stimulate the jawbone, which means they cannot prevent bone loss in the area of the missing tooth.
Additionally, because they depend on adjacent teeth for support, those teeth may become weaker or more prone to decay over time.
Cost Comparison: Implants vs Bridges
The cost of treatment is one of the most important factors patients consider when deciding between implants and bridges.
Dental implants generally have a higher initial cost compared to bridges.
This is because implants involve surgical placement, high-quality materials, and a longer treatment process that includes specialized imaging and planning.
However, implants are designed to last for many years and often require less maintenance over time, which can make them more cost-effective in the long run.
Bridges, on the other hand, are less expensive upfront and are usually completed more quickly. They are also more likely to be covered by dental insurance plans compared to implants.
While the lower initial cost of a bridge is appealing, it is important to consider that bridges typically need to be replaced every five to fifteen years depending on wear and oral hygiene.
Over a lifetime, the cumulative cost of replacing bridges can exceed the one-time investment of a dental implant.
When making a decision, patients should consider not only the immediate cost but also the long-term value and potential for additional dental work in the future.
Appearance and Comfort
Both dental implants and dental bridges are designed to restore the appearance of missing teeth, but there are differences in how they feel and how natural they look over time.
Dental implants closely mimic natural teeth because they are anchored directly into the jawbone. This provides a stable and secure foundation, so they do not shift or move when eating or speaking.
The crown is custom-designed to match the color, shape, and size of the surrounding teeth, creating a seamless and realistic appearance.
Many patients report that implants feel almost identical to their natural teeth, which makes them very comfortable.
Dental bridges also provide a natural look initially.
However, because they rest on top of the gums and are supported by neighboring teeth, changes in gum shape or slight movement of the supporting teeth can create small gaps over time. This can affect both the appearance and the comfort of the bridge.
While bridges are generally comfortable, they may not feel as secure as implants, especially when chewing harder foods.
Impact on Adjacent Teeth
One of the most significant differences between implants and bridges is how they affect the health of neighboring teeth.
Dental implants are standalone restorations. They do not rely on the surrounding teeth for support, which means the natural teeth next to the gap remain intact and unharmed.
This is an important benefit because it preserves the strength and structure of healthy teeth.
Bridges, however, depend on the adjacent teeth to hold the restoration in place. To fit the crowns, these teeth must be filed down, permanently altering their shape.
This makes them more vulnerable to decay, sensitivity, and structural damage in the future. Over time, this can lead to additional dental procedures, such as fillings or root canals, on the supporting teeth.
For patients who want to protect their remaining healthy teeth, implants are generally the better option.
Bone Health and Longevity
When a tooth is lost, the jawbone in that area begins to deteriorate because it no longer receives the pressure and stimulation provided by chewing.
This bone loss continues over time and can lead to noticeable changes in facial structure, such as a sunken or aged appearance.
Dental implants address this problem by acting like natural tooth roots. When a person chews, the implant transfers pressure to the surrounding bone, which helps maintain bone density and strength.
This stimulation prevents bone loss and preserves the natural contours of the face and gums.
Dental bridges, on the other hand, sit above the gumline and do not interact with the bone. Because of this, they cannot prevent the gradual bone loss that occurs after tooth extraction.
Over time, this may result in changes to the fit of the bridge and may even affect neighboring teeth and gums.
For patients concerned about maintaining long-term oral health and facial structure, implants offer a clear advantage.
Procedure Time and Healing
The amount of time required to complete treatment differs significantly between implants and bridges.
Dental implants involve multiple stages and typically take several months to complete.
After the implant post is surgically placed, there is a healing period of three to six months during which the implant fuses with the jawbone.
During this time, a temporary crown may be used. Once the healing process is complete, the permanent crown is attached.
While this timeline is longer, the result is a stable and permanent restoration that can last for many years.
Dental bridges are much faster to complete. The entire process usually takes two to four weeks and requires only a few dental visits.
Once the supporting teeth are prepared and impressions are taken, the final bridge is fitted and cemented into place.
This makes bridges an appealing choice for patients who want a quick solution without the need for surgery.
Maintenance and Oral Hygiene
Proper oral hygiene is crucial for both implants and bridges, but the maintenance required for each is different.
Dental implants are easy to care for because they function just like natural teeth. They can be brushed and flossed normally, and there are no special tools needed for cleaning.
Routine dental check-ups are important to ensure that the gums and bone around the implant remain healthy.
Bridges require more specialized cleaning techniques. Food particles and plaque can accumulate under the pontic, which increases the risk of gum disease and decay in the supporting teeth.
Special flossing methods or interdental brushes are often needed to clean under the bridge effectively.
Patients who find flossing challenging may prefer implants, as they are simpler to maintain in the long run.
Durability and Long-Term Value
Durability is another important factor to consider when choosing between implants and bridges.
Dental implants are highly durable and can last for fifteen to twenty-five years or even longer with proper care.
Because they are integrated with the bone and made from strong materials, they are resistant to many common dental problems, such as decay.
This long lifespan makes implants a valuable long-term investment.
Dental bridges, while reliable, generally have a shorter lifespan. Most bridges need to be replaced every five to fifteen years, depending on the patient’s oral hygiene and lifestyle habits.
Because the supporting teeth are still vulnerable to decay and wear, bridges may require additional repairs or replacements over time.
Although implants have a higher initial cost, their durability often makes them more cost-effective in the long run.
Risks and Complications
Both dental implants and dental bridges are safe treatments when performed by skilled professionals, but there are potential risks to be aware of.
Implants carry a small risk of complications, such as infection at the surgical site, implant failure if the bone does not fuse properly, or nerve or sinus issues in rare cases.
These risks are greatly reduced when the procedure is performed by an experienced dentist and when patients follow proper aftercare instructions.
Bridges have their own set of risks. Because they rely on adjacent teeth for support, decay or damage can develop under the crowns if oral hygiene is not maintained.
Gum disease is also a concern if plaque builds up around the bridge. Over time, the supporting teeth may weaken, which can lead to further dental problems.
Regular check-ups and consistent at-home care can help prevent most complications associated with either treatment.
Suitability: Who Should Choose Which?
The choice between implants and bridges depends on several factors, including overall oral health, bone density, lifestyle, and budget.
Dental implants are ideal for patients who have healthy gums and sufficient jawbone density.
They are also a great choice for individuals who want a permanent, low-maintenance solution and are willing to commit to a longer treatment timeline.
Implants are especially suitable for those who want to preserve their natural teeth and prevent future bone loss.
Bridges are better suited for patients who may not have enough bone to support an implant and do not want to undergo bone grafting surgery.
They are also a practical option for those who need a quicker, more affordable solution.
In cases where the adjacent teeth already require crowns or major restorations, a bridge can be an efficient way to address multiple issues at once.
A dentist will perform a thorough evaluation to determine which option best fits the patient’s needs.
Decision-Making Checklist
Making the right decision between a dental implant and a bridge involves careful consideration. Patients should think about their long-term oral health goals, budget, and willingness to undergo surgery.
Implants are the better choice for those seeking a permanent solution that protects bone health and neighboring teeth.
Bridges are a good alternative for those who prefer a quicker, less invasive, and more affordable option, especially when surgery is not possible.
By discussing your concerns and goals with a dental professional, you can make an informed decision that will provide the best balance of function, comfort, and aesthetics.
Conclusion
Replacing missing teeth is essential for maintaining oral health, function, and overall quality of life.
Both dental implants and dental bridges are effective solutions, but the right choice depends on a patient’s individual needs, long-term goals, and overall oral condition.
Dental implants provide a permanent and highly durable solution that closely mimics natural teeth. They protect surrounding teeth, prevent jawbone loss, and offer unmatched stability and comfort.
While they require a longer treatment timeline and higher initial investment, their longevity makes them a cost-effective option in the long run.
Dental bridges, on the other hand, are quicker to complete and more affordable upfront, making them a practical option for those seeking a faster solution.
However, they do not prevent bone loss and require the alteration of neighboring teeth, which can lead to future dental concerns.
Ultimately, the decision should be made with the guidance of a skilled dental professional after a thorough examination.
By understanding the advantages and limitations of both options, patients can make an informed choice that not only restores their smile but also supports their oral health and confidence for many years to come.
